September is Gynecological Cancer Awareness Month! 💪 The five main types are cervical, ovarian, uterine, vaginal, and vulvar cancer. Early diagnosis increases the chances of survival.
Gynecological cancer is a broad term for cancers that begin in a woman’s reproductive organs. These cancers start in the pelvis—the area below the stomach and between the hip bones.
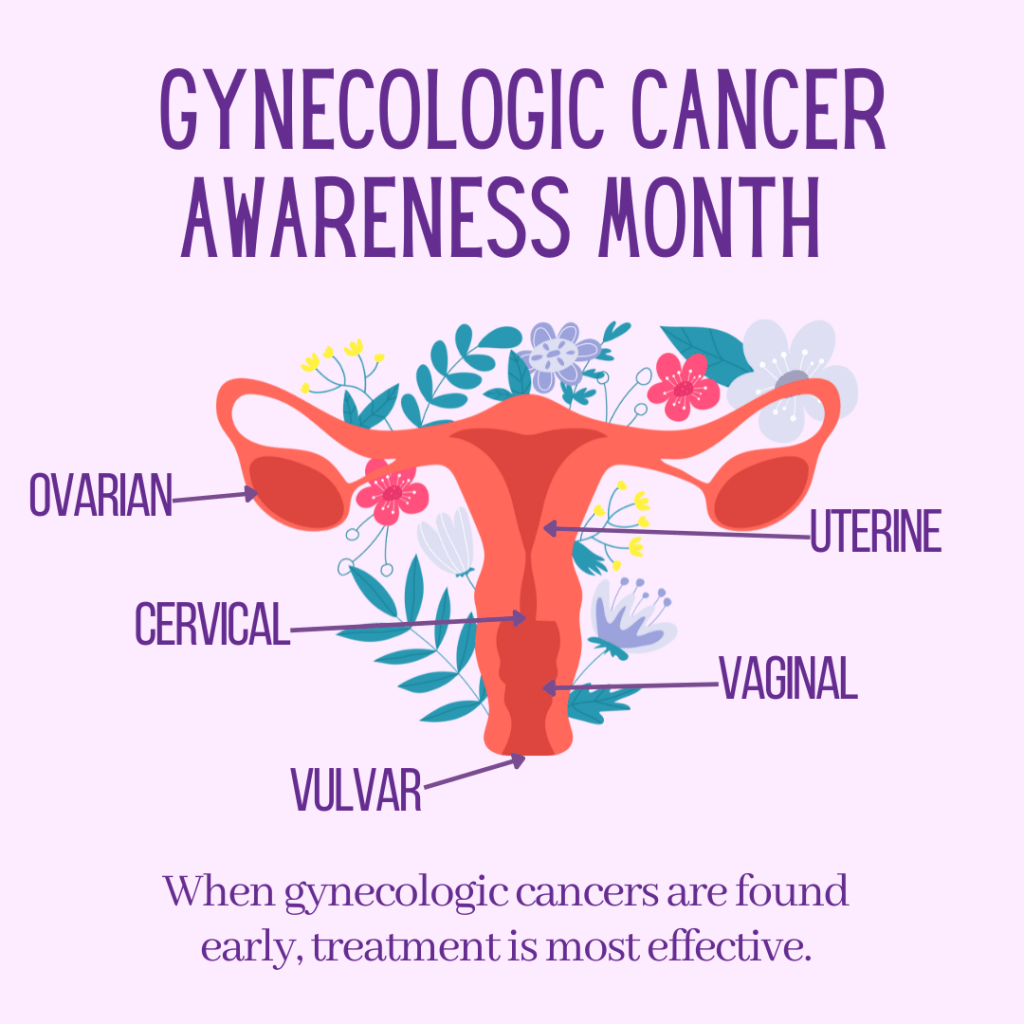
Types of Gynecological Cancer
The main types include:
- Cervical cancer – starts in the cervix (the lower part of the uterus).
- Ovarian cancer – starts in the ovaries.
- Uterine cancer (also called endometrial cancer) – starts in the lining of the uterus.
- Vaginal cancer – starts in the vagina.
- Vulvar cancer – starts in the outer part of the female genital organs (the vulva).
- Fallopian tube cancer – less common, starts in the fallopian tubes.
Risk Factors
- Family history of gynecological cancers
- Human papillomavirus (HPV) infection (for cervical cancer)
- Obesity and hormonal imbalances (for uterine cancer)
- Age (risk increases as women get older)
- Certain genetic mutations, like BRCA1 and BRCA2 (linked to ovarian and breast cancer)
Symptoms
Warning signs may vary by cancer type but can include:
- Abnormal vaginal bleeding or discharge
- Pelvic pain or pressure
- Bloating or feeling full quickly (especially with ovarian cancer)
- Pain during sex
- Changes in bathroom habits (urination or bowel movements)
- Persistent itching, burning, or soreness of the vulva
Prevention and Early Detection
- Regular screenings: Pap tests and HPV tests can detect cervical changes early.
- HPV vaccination: Protects against many cases of cervical, vaginal, and vulvar cancers.
- Healthy lifestyle: Maintaining a healthy weight, not smoking, and exercising can lower risk.
- Genetic counseling: For women with strong family histories, genetic testing may be recommended.
I am sharing this information as an ambassador of the National Cervical Cancer Coalition. For more information visit www.nccc-online.org/hpvcervical-cancer.

Leave a comment